- en
- nl
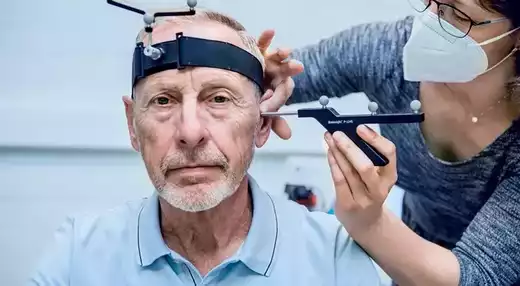
Innovation in healthcare is changing lives. Advanced technology and novel approaches are making care and treatments more effective and accessible than ever before.

The Biomedical Research Institute is a multidisciplinary institute of Hasselt University where high-end technologies are used to gain new insights into three disease domains: immunology, neuroscience and cardiometabolic disease.
More in detail, we aim to:

The Brussels Liver Research to Valorisation Consortium (B-Liver) brings together complementary expertise in liver cell biology, pathology, and toxicology from the liver research groups IVTD and LIVR at the Vrije Universiteit Brussels. B-Liver's core mission is firmly rooted in established models and technology. Still, it also ventures into higher-risk emerging innovations aimed at advancing liver modelling, predicting toxicity, and developing therapeutic strategies for liver diseases.

Immunotherapy, including vaccines, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells and checkpoint blockers, have produced extraordinary clinical results in subsets of cancer patients. Nonetheless, a number of patients do not benefit from immunotherapy, highlighting the need for strategies to improve its outcome. The INTEGRAL platform (“Integrating a multimodal approach to address current challenges in immunotherapy”) combines the complementary offering of expertise, know-how, knowledge and technologies originating from the VUB ICMI, CMIM and LMCT laboratories, to address this issue by offering tools for combining immune activation (ACTIVATION) with negating immunosuppressive cues (MODULATION), steering drug development (cellular and molecular MODE OF ACTION analysis) and driving patient selection and monitoring of therapy response (via in vivo IMAGING).

During (cancer) surgery, the surgeon can merely rely on visual inspection. NLITE aims to investigate novel intraoperative imaging applications based on fluorescence lifetime (FLT) and nanobody-based molecular fluorescence tracers. More specifically, it tries to conceive a unique video-rate FLT imaging system that will boost the applications of the clinically available fluorescent dyes or that can be used in combination with dedicated nanobody-based tracers. Ultimately, this will improve surgical accuracy, influence decision-making on a per patient basis and reduce surgically-induced side effects.

The µFlow Cell is focused on medical, pharmaceutical and biotech applications, and aspires cooperation with industry along three routes:
1. design and develop innovative microfluidic solutions within the core research lines of the consortium
2. fabricate and validate microfluidic devices and microreactors, from prototype to small industrial series
3. engineer and produce functional microparticles, such as biomaterials for therapeutic or diagnostic procedure, from lab to small industrial scale.
The µFlow Cell has a dedicated team of experts and technicians with access to internal and external cleanroom facilities equipped with advanced micro- and nanofabrication processes.

The aim of the TOPGUN program is two-fold. Firstly, the development of new peptide-based molecules that can be used in cancer diagnostics. Our aim is to develop these molecules by translating existing nanobodies (single-domain camelid antibodies) into peptide-based therapeutics, which are smaller, cheaper and easier to produce. We would design these in a way that they maintain or improve upon the functional activity held by the nanobodies from which they are derived. In doing so, the drawbacks held by nanobodies will be reduced or eliminated, and the costs to produce and use such molecules clinically will be substantially reduced. Secondly, as a partly linked valorisation pathway, we aim to use and valorise the facilities at the Brussels Imaging Pharmacy (BIP) to be used by third party research groups and/or companies in Flanders and beyond for Radiopharmacy that would not be possible in their own facilities.

The NEUR-o-AIMS consortium aims to improve the prediction of cognitive decline in neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular brain diseases through the development of novel biomarkers, that allow to improve the understanding of the underlying disease processes. In doing so, the NEUR-o-AIMS consortium aims to translate the results of these lines of fundamental research into better diagnostic tools, the identification of druggable targets and improved treatment options.

The Lab for Molecular Biodiscovery is interested in the identification and validation of novel small molecules with significant pharmacological potential using a zebrafish-based platform, with a special interest in small molecules from natural sources. The lab has major efforts underway to find hits with novel chemical structures in the areas of epilepsy and BMP/Wnt signaling.

The Medical Imaging Research Center is an interdisciplinary research center with a central location in the University Hospital Gasthuisberg. It is surrounded by the different clinical imaging departments yielding easy access to the state-of-the-art imaging equipment and patient data. The focus lies on fundamental and translational research in the area of medical imaging and image processing.

The lab of Cardiovascular Imaging & Dynamics focuses on developing, validating, and applying new imaging methodologies that can help obtain insight into the (patho)physiology of the heart and contribute to a better diagnosis and therapy of the individual cardiac patient. Being located at the core of the clinical imaging modalities of the university hospital, access to imaging data and scanners is highly facilitated.

MIRaCLe (Molecular Imaging Research and Clinic Leuven) is a centre of excellence for pre-clinical and clinical molecular imaging and provides an integrated approach going from tracer development, over GMP production to (pre)-clinical validation and applications. The centre unites key experts in radiopharmacy, nuclear medicine and image analysis of both KU Leuven and UZ Leuven. It combines this multidisciplinary expertise with state-of-the-art infrastructure that can be applied for drug development, clinical trials and fundamental research studies.

The complexity of underlying molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of human disease is a major challenge in drug discovery today. At the laboratory for Molecular Virology and Gene Therapy the translation of solid basic research into innovative therapies has always been the ambition. Starting from our decade long expertise in HIV virology and cell biology, with a focus on LEDGF/p75, an epigenetic reader, we validate novel targets for drug discovery in the fields of HIV Cure, leukemia and Rett Syndrome.

Since its establishment in 1954, the Rega Institute has played a leading role in the fight against bacterial and viral infections, immunological disorders, and other conditions. In collaboration with a lab in Prague, Rega researchers described the effect of the HIV inhibitor tenofovir. It’s been on the market since 2001 and is still the world’s most frequently used anti-HIV medicine.

PharmAbs wants to bridge discovery and valorization with antibodies. The center's objective is to support academic groups and biotech companies in creating value for their project by generating tailor-made antibodies, by demonstrating in vivo proof-of-principle and initiate development towards the market. PharmAbs is a technology-based research center applying a product-focused and market-oriented strategy. It also offers affordable fee-for-service solutions to universities and companies.

The Centre for Drug Design and Discovery (CD3) is a drug discovery centre and investment fund created to drive the translation of innovative basic research to the clinic. As investment fund, CD3 can invest in drug discovery projects as well as in spin-off companies and biotechs, while as drug discovery centre, it complements investments with an experienced drug discovery team and state-of-the-art infrastructure.
The cornerstone of CD3’s activities are hand-in-hand collaborations with academic research groups and biotech or pharma partners, always aimed at discovering and developing new medicines.

Since its establishment in 1954, the Rega Institute has played a leading role in the fight against bacterial and viral infections, immunological disorders, and other conditions. In collaboration with a lab in Prague, Rega researchers described the effect of the HIV inhibitor tenofovir. It’s been on the market since 2001 and is still the world’s most frequently used anti-HIV medicine.

The division of Skeletal Tissue Engineering (Prometheus) of KU Leuven is an interdisciplinary initiative focusing on skeletal tissue engineering (TE) research and technology transfer. The Prometheus platform runs three integrated programs:

The KU Leuven Institute for Single Cell Omics (LISCO) nucleates interdisciplinary expertise in single-cell multi-omics to investigate normal development, aging and disease processes in humans and other organisms, down to the biology of unicellular life forms.
LISCO aims to develop innovative single-cell analysis technologies and high throughput platforms to enable breakthrough biological and biomedical science that transcends an individual research lab, to pioneer and set standards in disruptive single-cell technologies and research, and to translate technologies and biomedical discoveries to the clinic. It creates a framework for academic and industrial collaboration, service provision, and training of the next-generation researchers.
LISCO unites researchers from KU Leuven, UZ Leuven and VIB-KU Leuven.

More info on the Department of Human Genetics' website.

The Leuven Cancer Institute conducts pioneering cancer research by combining the forces of KU Leuven, UZ Leuven and VIB-KU Leuven Center for Cancer Biology. The patient and its tumor are central in our research cycle. The range of activities is very broad: from fundamental research into the pathological mechanisms of cancer to translational research into new methods for diagnosis and treatment, and clinical studies in patients. With this approach, we aim for better prevention, faster detection, and more targeted treatment.

Leuven Viral Vector Core (LVVC) is a full-service facility dedicated to the development of customized viral vectors for life science purposes. The core strengths of the LVVC are:
The LVVC provides expert consulting tailored to your
specific project and is continuously involved in bilateral contracts with universities, research institutions and industry.

IMARK aims at expediting biomarker discovery and development by resolving molecular and structural patterns in space and time. IMARK capitalizes on the deeply rooted expertise in biomedical imaging at the University of Antwerp and his pre-decesor EGAMI to push the boundaries of precision medicine.
To this end, it unites research groups with complementary knowledge and tools that cover all aspects of imaging-centred fundamental research, preclinical validation and clinical evaluation.
IMARK harbours high-end infrastructure for electron and light microscopy, mass spectrometry imaging, magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, positron emission tomography and single-photon emission computed tomography.
Moreover, IMARK members actively develop correlative approaches that involve multiple imaging modalities to enrich information conten

PreMeT (Precision Medicine Technology) aims to enable precision medicine through an integrated approach of genomics and big data analysis.
Precision medicine is an approach to tailor healthcare individually, on the basis of the genes, lifestyle and environment of an individual. It is based on technologies that allow clinicians to predict more accurately which treatment and prevention strategies for a given disease will work in which group of affected individuals. Key drivers for precision medicine are advances in technology, such as the next generation sequencing technology in genomics, the increasing availability of health data and the growth of data sciences and artificial intelligence.
In these domains, multiple strong research teams of the UAntwerpen joined forces to translate their research and offer a technology platform for precision medicine towards industry, hospitals, research<

VAXINFECTIO was established as a formal Institute of the Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences of the University of Antwerp in 2007 to promote the multidisciplinary research of vaccines and infectious diseases.
Since January 2008 VAXINFECTIO is formally recognized as one of the five Centre’s of Excellence of the University of Antwerp.
Additionally, a new collaboration between VAXINFECTIO and the Evolutionary Ecology Group at the department of Biology, Faculty of Science, was recognized as new Centre of Excellence called ASCID (Antwerp Study Centre for Infectious Diseases).
VAXINFECTIO is also holder of Industrial Research Funding (IOF) together with the Faculty of Design Sciences, Department of Product Development (IOF consortium VAXINFECTIO-PO), which major focus on applied/industrial research,&

The Biomedical Research Institute is a multidisciplinary institute of Hasselt University where high-end technologies are used to gain new insights into three disease domains: immunology, neuroscience and cardiometabolic disease.
More in detail, we aim to:

The REVAL research group of the Faculty of Rehabilitation Sciences at Hasselt University focuses on interdisciplinary and technology-supported research within rehabilitation, with attention to clinical applications in practice. The individual is central with the aim of promoting the functioning, health and well-being of every person. Contract research is also possible via the ReLab service platform.

Structural Biology Brussels (SBB) studies the structure of proteins and DNA from the molecular to the atomic level. By determining the position of atoms in a macromolecule (proteins, for example, contain thousands of atoms) we can derive how such molecules can act as tiny machines, and determine how they interact with each other. The end goal of this research is to unravel the complex machinery that makes cells work.

Provaxs is the business development center of Ghent University for innovation in animal health. It is our ambition to advance animal care by combining scientific expertise, knowledge and know-how on animal health with an entrepreneurial organisation of scientists and experienced tech-transfer professionals.

Victoris, the Valorisation Centre for Technological Optimization, Research and Innovation in Sports, represents more than 40 researchers active in a diversity of sport topics. The final goal of each member of the consortium is to support people in the best possible way by creating products & services based on science. This may include sensor and digital technologies, textiles or insoles and braces, and nutrition and supplementation. In order to realize this objective, we set up partnerships with companies, startups, clubs, federations, governments, etc.

Gene therapy has significant potential to cure disease and alleviate human suffering. In this IOF project, VUB focuses on developing and validating next-generation gene therapy to maximise the therapeutic benefits for the patients and minimize potential side effects. The project’s ultimate objective is to consolidate a new technology platform with potentially broad implications for clinical and industrial valorisation.

Biomarked is a network of 33 research groups with a focus on preclinical biomarker research, development of biomarkers for diagnostic tests or therapy and interaction of microbiome with diseases/therapy. Our expertise includes platform technology for biomarker identification and characterization (metabolomics, proteomics, (epi)genomics, glycomics, EV-CORE expertise center, ddPCR expertise center, O-LINK platform, study of the biological clock, CRISPR array screening platform), as well as bioinformatics and development of pre-clinical in vitro assays (Cuboids, Spheroids, metastatic assays, organoids).
In our project portfolio we have projects in precision medicine, screening and therapy monitoring of cancer, metabolic diseases, HIV, IBD, as well as interaction between microbiome and various disease patterns. Therapeutic projects in pre-clinical development include biological therapy for various eye diseases, gene therapy/ASO therapy for retinal eye diseases and cancer. We support the CRIG platform (Cancer Research Institute Ghent) and the GATE platform (Gene Cell Tissue Engineering).

The goal of HyCT - Hybrid Computed Tomography in physical and life sciences is to push technology to the market, pro-actively look to pull-in maturing technologies, and start co-creation partnerships with industry.
In 2007, Ghent University founded the Hybrid Computed Tomography valorization cluster (or HyCT) under the umbrella of the Flemish Industrial Research Fund (IOF). Springing from two core facilities UGCT (X-ray imaging in physical science) and MEDISIP (CT, PET and SPECT hardware in life sciences), the current members consist of 12 Ghent University research teams. Five are working on tomographic imaging hardware (1D to 4D), signal and image processing for material sciences and life sciences in the broad sense. Seven supporting groups range from electronics over clinical departments to veterinary specialists.

MedTeG - Medical Technology Ghent facilitates and supports the development of new, innovative medical technologies through its robust ecosystem in Ghent, with a strong network across the country and beyond.. MedTeG was founded on the common vision to grow Ghent into a thriving MedTech hub.

The ACT-T - Advanced Cell & Tissue Engineering consortium unites researchers and doctors from Ghent University and Ghent University Hospital on gene, cell and tissue therapy. It supports and is a co-founder of the GATE - Ghent Advanced Therapies and Tissue Engineering platform.

DISCOVERE directly supports CRIG researchers in their efforts to mature and validate their inventions into an attractive drug or technology asset for the benefit of cancer patients. In addition, DISCOVERE provides business development services to set-up partnerships with industry and aims to act as an organizational point-of-entry for companies in search for specific solutions for their own drug discovery, drug delivery or drug manufacturing projects.